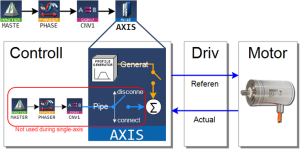
Axis Pipe Block
The Axis pipe block is the link between the logical and physical worlds, managing position data for a physical or simulated axis.
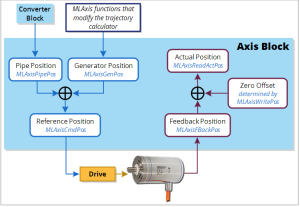
Figure 1: Axis Pipe Block Positions
Jump to a section on this page:
Associated Data on Positions
This data are illustrated here:
-
-
All positions are in user units with modulo applied if active, unless specified.
| Position / Offset | Description |
|---|---|
|
This is the actual position of the underlying axis as reported by the drive.
ActualPos := FeedbackPos + ZeroOffset |
|
|
This is the current position the drive reports for an axis, scaled to user units. It does not take into account the value of the Zero Offset or axis modulo. |
|
|
This is the summation of all previous commands (i.e., calls to functions which perform motion) to the Axis internal motion generator. See either such as MLAxisAbs, MLAxisMoveVel, or MLAxisRel.
|
|
|
This is the output of the convertor block is written into the Pipe Position value whenever the Convertor block is connected to the axis and the pipe is active. See Convertor. |
|
|
This is the commanded axis position sent to the drive. It is the summation of Pipe Position and Generator Position. ReferencePosition = Pipe Position + Generator Position |
|
|
This adjusts the coordinate system so the Actual Position reports correct values after homing or using MLAxisWritePos. |
Axis Block Initialization
A call to the MLAxisInit function block is required to implement motion for the axis.
- All positions and offsets are set to zero.
- The Axis Block motion generator is initialized with the proper ranges.
- Values are aligned: ReferencePosition = Pipe Position + Generator Position.
Axis Connection to a Pipe
A call to the MLCNVConnect function block is required to get motion generated in the pipe to the Axis.
- Pipe Offset calculation is: Pipe Offset = Pipe Position – Reference Position.
- Values are aligned: ReferencePosition = Pipe Position + Generator Position.
Change Axis Position Functions
Homing
Homing is the process of moving the motor to a known physical reference point on the machine.
- Homing can be performed with the MLFB_Home* Kollmorgen UDFBs or by adding custom application code that uses only the Axis function blocks.
- The Pipe Network is typically not used in homing.
- Custom homing is done with MLAxisRel and MLAxisAbs to make motion and MLAxisWritePos to set a position offset.
Monitor an Axis
These are the function blocks to monitor the performance and status of an axis.
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Returns the reference position of the axis. |
|
|
Verifies if an axis is ready. |
|
|
Returns the actual position of the axis. |
|
|
Returns the status of the internal generator of the axis. |
|
|
Returns the status of the axis. |
Multi-Axis Operation
For multi-axis applications, automatic operation requires both:
- Motion synchronization between two or more axes.
- The Pipe Network is required to achieve the synchronization.
To start up the Pipe Network, these two function calls must be executed in an application program:
PipeNetwork(MLPN_ACTIVATE): PipeNetwork(MLPN_CONNECT);
Multi-axis synchronized motion is accomplished using a motion block associated with one of these input Pipe Blocks:
- Master: MLMstRun, MLMstRel, and MLMstAbs
- PMP: MLPmpAbs, MLPmpRel
- Sampler: MLSmpConnect, MLSmpConECAT, MLSmpConPNAxis, MLSmpConPLCAxis
Realign Positions
A call to the MLAxisReAlign function block is used to realign the axis after an error occurs
- Motion must come to a stop first.
- The MLAxisReAlign is executed.
You must set the movement of this block to MLAxisReadActPos - MLAxisCmdPos. - The target position must be reached before any additional motion can occur.
It can be checked by using the MLAxisReAlgnRdy function block.
Set Zero Axis
A call to the MLAxisWritePos function block is used to set a position offset at the Axis when the Pipe Network is not yet connected.
- Pipe Position and Pipe Offset are set to zero.
- Generator Position is set to equal to Zero Position.
Zero Position is defined in MLAxisWritePos function block. - Then ReferencePosition = Pipe Position + Generator Position.
Single-Axis Operation
This includes motion done on an individual axis block: jogging, absolute move, or incremental moves.
- If these are single-axis based, then motion is executed with the MLAxisMoveVel, MLAxisAbs, and MLAxisRel FBs.
- These motions are typically done during machine setup or adjustment and are often referred to as manual mode.
- For these operations, the Pipe Network does not need to be connected to the axis.
Units
User Units (abbreviated UU) are dimensions used in the application code to define axis position or distance for an axis.
The User Units per Revolution field is used to set how many of these custom units are associated with one revolution of the motor.
Examples
|
User Units |
User Units per Revolution Value |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Degrees |
360.0 |
|
|
Gradians |
400.0 |
|
|
Inches |
15.7079632679489662 |
This equals pi*5. This could represent the circumference of a 5 inch diameter drum. |
|
Radians |
3.14159265358979324 |
|
KAS standard units for velocity and acceleration are UU/sec and UU/sec2.
View Axis Block Position Functions
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Returns the reference position of the axis. |
|
|
Returns the generator position of the axis. |
|
|
Returns the pipe position of the axis. |
|
|
Returns the actual position of the axis. |